Mechanical Compression Devices For Dvt Prophylaxis

Outpatient use of compression devices following hospitalization with or without pharmacologic prophylaxis has also been proposed.
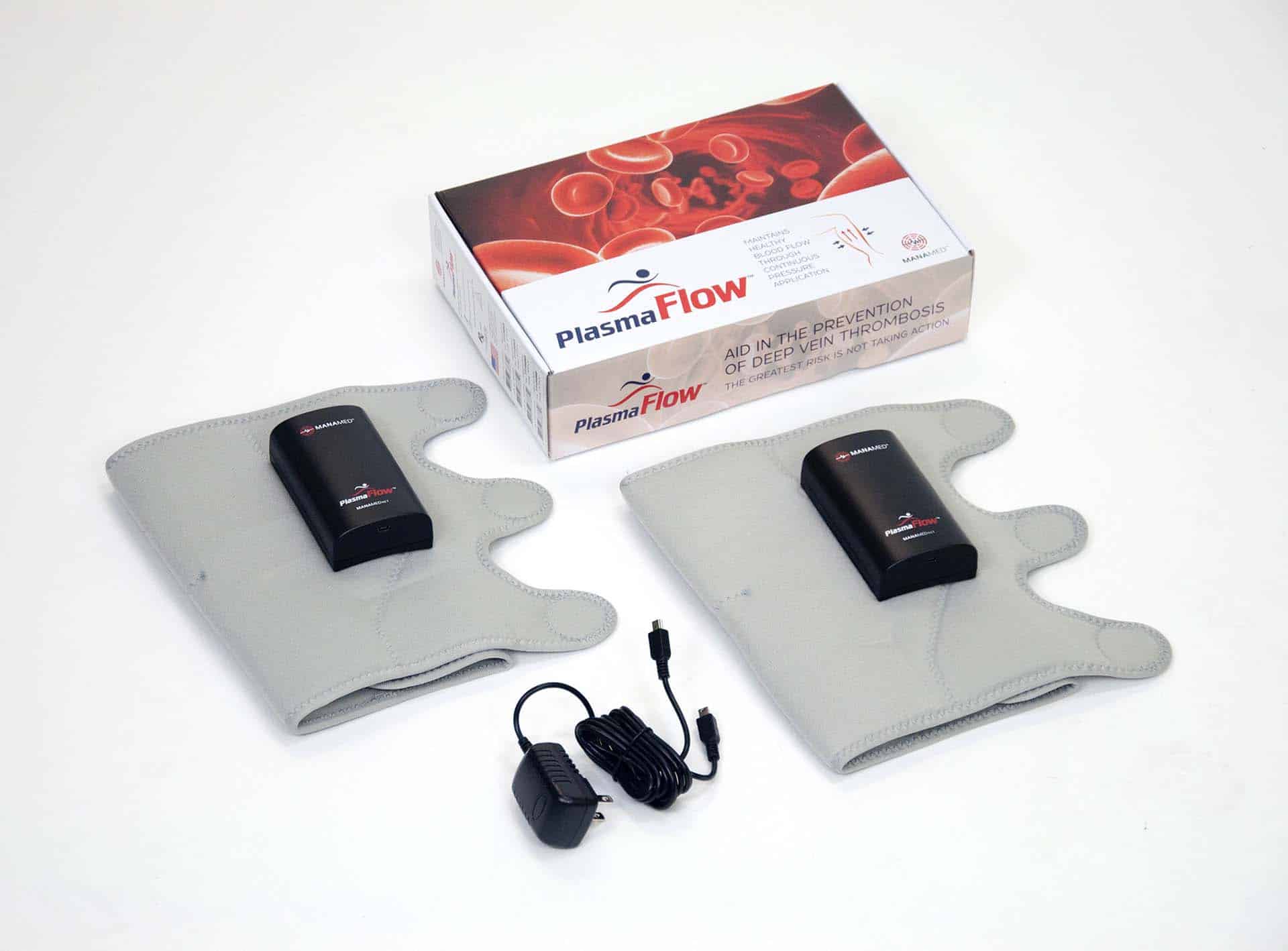
Mechanical compression devices for dvt prophylaxis. In the pneumatic compression for preventing venous thromboembolism prevent trial arabi and colleagues found that use of adjunctive. 1 2 the average annual incidence of dvt in the united states ranges from 48 to 122 per 100 000. This increases blood flow through the veins of your legs and helps prevent blood clots. Manufacturer of mechanical dvt prophylaxis sequential compression device offered by st.
These antithrombotic regimens include pharmacological interventions and mechanical techniques to counteract venous stasis including graduated compression stockings and intermittent pneumatic compression ipc devices. Luke med devices pvt ltd chennai tamil nadu. Pulmonary embolism pe resulting from deep vein thrombosis dvt collectively known as venous thromboembolism vte affects an estimated 900 000 americans each year and results in significant morbidity and mortality. There are different opinions about whether or not prophylaxis should be used in knee arthroscopy partly reflecting different perceptions of the underlying risk of dvt.
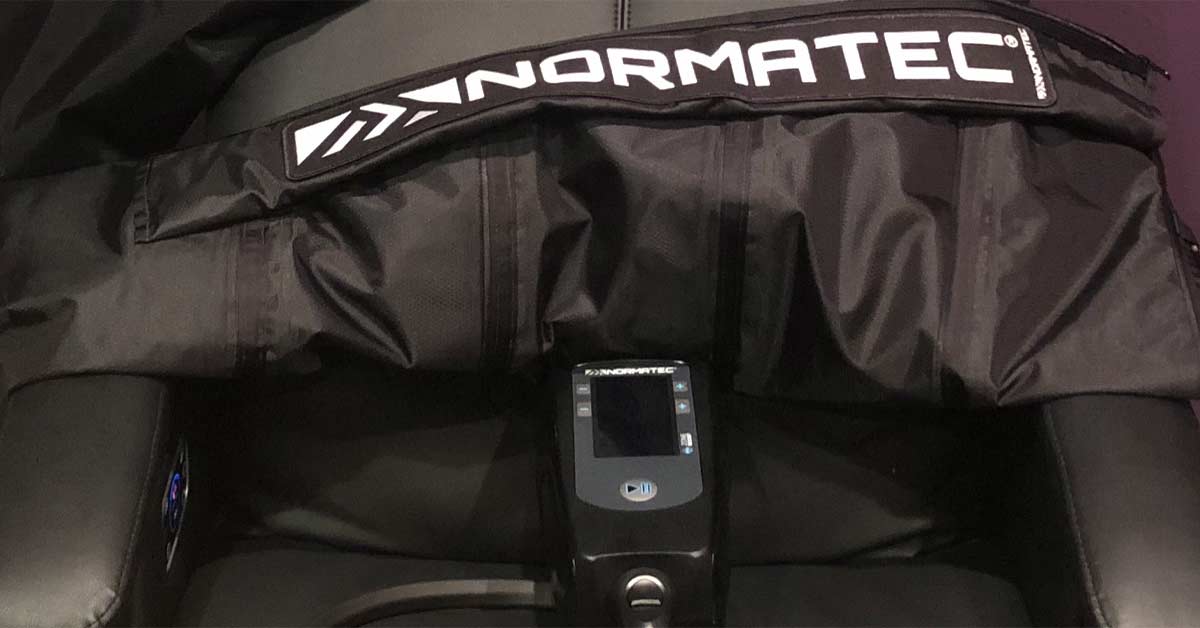
There exists a considerable range of potential prophylactic measures aimed at reducing the risk of vte. Although pharmacologic prophylaxis has been shown to reduce the incidence of deep vein thrombosis evidence is limited on the combined use of mechanical compression devices and pharmacologic prophylaxis. Intermittent pneumatic compression ipc devices are used to help prevent blood clots in the deep veins of the legs. 1 2 with the ageing u s.
The devices use cuffs around the legs that fill with air and squeeze your legs. 3 in addition compression solutions has made this type of treatment easy for patients to use at home with our compact and portable triple play vt. Recently published results showed superior deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis among patients who underwent mechanical compression device therapy for up to 6 weeks after limited tourniquet total knee. It is safe and effective with no side effects.
Pharmacological options include anticoagulation eg low molecular weight heparin lmwh new oral anticoagulants or warfarin and aspirin but these may increase the risk of bleeding. Mechanical prophylaxis with intermittent pneumatic compression devices ipcds. Antithrombotic prophylaxis is recommended for surgical patients who are at moderate to high risk of postoperative venous thromboembolism vte including deep vein thrombosis dvt and pulmonary.